Diodes
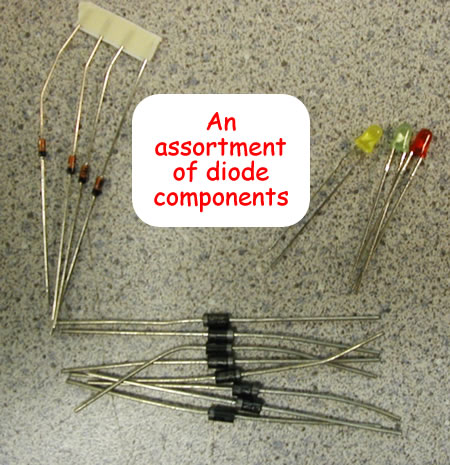


You should be able to draw this from memory.
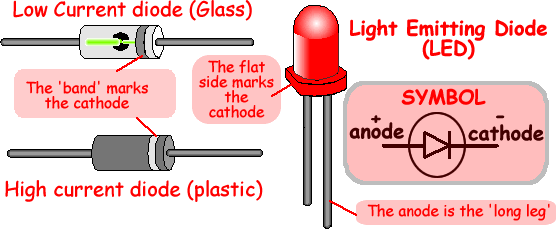
If there are arrows coming out of it, it is called a 'light emitting diode' or LED. This is the type of diode that lights up when it is conducting electricity.
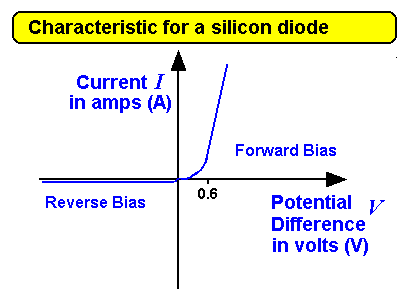
You should know this curve and be able to 'interpret' this characteristic that means explain how it shows that:
- The current through a diode effectively only flows in one direction only.
- It's resistance is very low when connected in forward bias as long as it has a potential difference of more than 0.6 volts (this varies but is usually about 0.6 to 0.7 volts) across it.
- The diode has a very high resistance when it is connected in 'reverse bias' - the opposite direction - therefore only a tiny current flows when this is the case.
You should note that:
- At 0V no current flows.
- At +0.6V the forward current starts to rise sharply.
- At -ve voltage there is a tiny current.
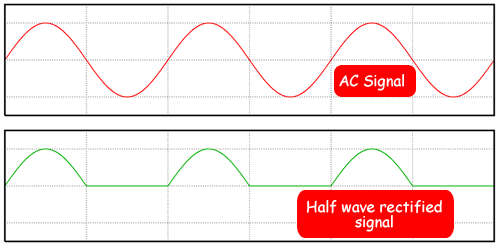
When connected into a circuit in forward bias the diode is simply like a conductor wire - it has such a low resistance that it hardly affects current flow..The p.d. across the diode in a circuit is about 0.6V (it's operating voltage - sometimes the question will state that it is 0.65V or 0.7V). So when analysing circuits you have to remember this. Sometimes the examiner will give you a graph to read the operating voltage from.When connected in reverse bias the diode acts like an open switch in the circuit (it has a very high resistance) so all of the components on that strand will have a negligible current flowing through them - bulbs will effectively be 'off' because so little current will flow that they will not light up.Like a resistor, the diode has only two connectors. One is called the anode (it is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply), and the other is called the cathode (it is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply). The diagram below shows drawings of different types of diodes and their electronic symbol.Notice how the cathode side is marked with a ring or band the ordinary diodes and a flat side and/or short lead because it is important that the diode is connected the correct way round.AC Supply and the DiodeWhen alternating voltage is applied across a diode, it will convert the alternating current (AC), which flows back and forth, to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction - but it only does that for half of the cycle - we say it rectifies the current.It only allows half of the current signal to get though.
aymeric
dis is sick bruv.
ReplyDeletethums up