1-Explain how a fuse works and determine the correct fuse for an electrical device.
2-Define the kilowatt-hour.
Keywords (page 108-109 in the orange book):
1-Current is a flow of current, measured in ampere(A).
2-Power is the rate of doing work, measured in watts(W).
3-Fuse is an electric component designed to heat up, melt and break a circuit.
4-Joules is an unit of energy (J)
5-Kilowatt-hour is an unit of energy(KWh)
Fuse
A fuse is an electrical component that is designed to heat up, melt and break the circuit (to stop the current) when a specified amount of electric current passes through it. It is used as a safety device.
The fuse breaks the circuit if the current is too high. this protects the component and the user if something goes wrong.
there are three common types of fuses and they are 3A, 5A and 13A.
The fuse used should be slightly higher than the current passing through the component such as a 3A fuse should be used for a current of 2A.
How to
chose which fuse to use:
P=VI
P-Power in
watts(W)
V-Voltage
(V), the standard voltage is 230V in England
I-Current
in amps(A)
 |
| The 3 types of fuses used |
The circuit breaker
The circuit breaker does the same job as the fuse, but works in a different way. A spring-loaded push switch is held in the closed position by a spring-loaded soft iron bolt. An electromagnet is arranged so that it can pull the bolt away from the switch. If the current increases beyond a set limit, the electromagnet pulls the bolt towards itself, which releases the push switch into the open position.
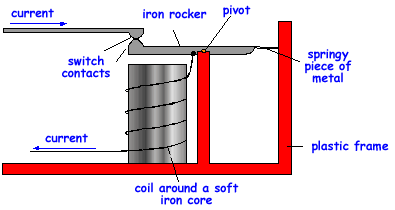 |
| A circuit breaker. |
 |
| A circuit breaker in a home. |
Kilowatt-hour
A kilowatt-hour (KWh) is 1000 watts used for 3600 second (constantly) it is therefore 3 600 000 J. This is because 1KW=?J/t
KW-Kilowatt
t-Time (s)
?J-Unknown energy (this become KWh when re-arranging the formula to become KWh=KW/t).
E
|
P
|
t
| ||
Remember the power must be in kilowatts (thousands of watts - in all other physics calculations it must be in watts)
|
Remember the time must be in hours (in all other physics calculations it must be in seconds)
|
 |
| This monitors how many Kilowatt-hours you use at home. |
1KWh costs 12p (£0.12). to work out how much 23KWh cost all you have to do is 23*0.12=£2.76
Questions-(Rember to use the standard of 230V)
Awnser questions in the comment area below.
Fuses
Kilowatt-hour
By Harshil
Current is the rate of flow of electrical charge (Not flow of current)
ReplyDeleteA fuse is designed to melt when the current becomes too high, due to the temperature increase created.
When the switch is opened, or tripped, on a circuit breaker this stops the flow of current. This can easily be reset by flicking a switch, whereas a fuse would need to be replaced. This is an advatage of circuit breakers over fuses.